In order to understand this topic it is important to understand the basic anatomy of the spine. Please review the section on basic spine anatomy before reading this section. To understand how the spine works, please review the section on the basic spine biomechanics.
What is a back strain?
The term “back strain” is used to describe an injury to the muscles and/or ligaments of the lower back. In this article the term back strain is used but the term “back sprain” can also be used to mean the same thing.
What are the functions of the muscles and the ligaments of the lower back?
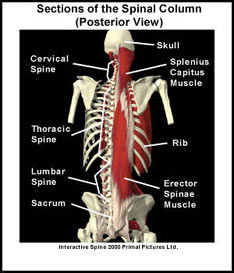
The complex anatomy of the lumbar region of the spine (low back) allows it to perform various functions. The lumbar region supports the weight of the body, protects the spinal cord and it allows the body to move by providing attachment sites for muscles. The muscles located closest to the vertebrae (back bones) help to provide stability to the spine. The muscles located further from the vertebrae play a role in movement of the spine.
Ligaments are like strong ropes that help connect bones and provide stability to joints. Six major ligament groups run down the spine and the low back. These ligaments attach to each vertebra and form a strong support system for the spine and the low back.
Why do low back strains happen?
The low back is subjected to high amounts of stress with bending, twisting and/or lifting activities. In certain cases the muscles and ligaments around the spine can become injured during a single activity such as lifting, or the back can become injured during a repetitive task. If the muscles and ligaments around the spine are stretched too far, or have too much load placed on them, it may result in small tears in the tissue and a microscopic amount of bleeding.
Injuries in the lower back are common in people who have a previous history of lower back injuries, and with people who have weak abdominal and back muscles.
What does a back strain feel like?
There is usually pain and tenderness around the muscles or ligaments that are injured. The affected muscles may also tighten up to protect the injured area. People with back strains usually do not complain of the following problems:
• Changes in the way their bowels and/or bladder work.
• Weakness in their leg muscles.
• Loss of leg muscle endurance.
• Pain and numbness that travels down either leg.
• Pain that is made worse by sneezing, coughing, or sitting down.
• Pain that is associated with fevers, weight loss, or anything else that suggests that they are feeling unwell.
• Pain that wakes them up at night, or is worse when lying down.
People with these warning signs need to see a doctor about their back pain right away.
How is a back strain diagnosed?
The first step in the diagnosis of a back strain is to obtain a good medical history and perform a physical examination. X-rays of the lower back may help to rule out degenerative disc disease. X-rays may be completely normal. Depending on the severity of the problem, further tests such as MRI and CT scans may also be required to rule out other causes of low back pain.
What is the treatment for a back strain?
In most cases, the damaged muscles and ligaments will begin to repair themselves. It is usually recommended that people consult with their doctor or physical therapist to help guide them back to health.
Available treatments include physiotherapy to learn proper movement patterns, education on activity modification, proper posture, and exercises. Physiotherapy may also include manual mobilization/manipulation of the affected area, and modalities such as gentle electrical currents and heat or ice to help with pain. Medications may also be an important part of the initial treatment. Doctors may prescribe anti-inflammatory medications, pain medications and/or muscle relaxants.
After someone recovers from a back strain it is important to maintain a healthy back with proper lifting techniques, proper posture, and exercises to maintain strong stomach and back muscles. These measures may help to decrease the chance of another back strain. Doctors and Physical Therapists that deal with people with back strains can help outline an individualized treatment and recovery program.
What other information is available on back strains?
Visit Back Pain Info / Neck Pain Info’s section on disc herniations for more information on this topic. Back Pain Info / Neck Pain Info’s links section has additional information on disc herniations and sciatica. Links have been provided to other websites as well as online medical journals. Visit Joint Pain Info. Com for information on other joint injuries and problems.
